Can Turtles Develop Fungal Digestive Infections From Gut Bacteria Deficiency?
Can turtles get fungal infections in their digestive system due to a lack of beneficial gut bacteria? Yes. Like humans, turtles rely on a diverse and balanced gut microbiome for their health. Without beneficial bacteria, their digestive system becomes vulnerable to harmful fungi. In this article, we will discuss the connection between turtles, gut bacteria, and the risks of fungal infections. Let’s explore turtle gut health.
Can turtles get fungal infections in their digestive system from a lack of beneficial gut bacteria?
The Importance of Beneficial Gut Bacteria in Turtles
Turtles, like many other organisms, have complex microbiomes that play a crucial role in their overall health and well-being.
The gut bacteria in turtles, also known as the gut microbiota, comprise a diverse and highly specialized community of microorganisms that reside in their digestive system.
These beneficial bacteria assist turtles in various ways, including aiding digestion, enhancing the immune system, and preventing the colonization of harmful pathogens.
One of the key functions of gut bacteria in turtles is digestion. Turtles are ectothermic animals, meaning their body temperature depends on the surrounding environment.
Consequently, their metabolism is relatively slow, and they rely on gut bacteria to effectively break down complex food particles and extract nutrients.
The gut bacteria produce enzymes that can break down otherwise indigestible components such as cellulose, enabling turtles to obtain vital nutrients from their food.
The Relationship Between Gut Bacteria and Fungal Infections
Fungal infections in turtles can occur when there is an imbalance or disruption in their gut microbiota. The gut bacteria help maintain a healthy environment in the digestive system by competing with harmful microorganisms for resources and space.
When the population of beneficial gut bacteria decreases, it creates an opportunity for opportunistic pathogens like fungi to thrive and cause infections.
Fungi are widespread, and many species can exist as commensals (harmless) or opportunistic pathogens. Under normal circumstances, the presence of beneficial gut bacteria can inhibit the growth of fungi and prevent them from becoming pathogenic.
However, when the balance is disrupted, either due to external factors or internal imbalances, fungi can multiply rapidly and cause infections in the digestive system of turtles.
Factors Contributing to a Lack of Beneficial Gut Bacteria
Several factors can disrupt the population of beneficial gut bacteria in turtles, ultimately leading to a higher risk of fungal infections. These factors include:
1. Diet
Turtles are known to be opportunistic feeders, consuming a wide variety of food items in their natural habitats. However, in captivity, their diet is often limited, and may lack essential nutrients and fiber.
A poor diet can hurt the diversity and abundance of beneficial gut bacteria, creating an imbalance that favors the growth of fungi.
2. Antibiotic Use
In some cases, turtles may require antibiotic treatment to combat bacterial infections. While antibiotics are effective in targeting harmful bacteria, they can also disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, leading to a decrease in beneficial species. This imbalance creates an opportunity for fungi to proliferate and cause infections.
3. Stress
Stressful conditions, such as inadequate habitat, improper temperature, or handling, can weaken a turtle’s immune system and alter its gut microbiota.
Changes induced by stress in the gut environment can disrupt the balance of beneficial bacteria, leading to the proliferation of fungi.
Prevention and Treatment of Fungal Infections in Turtles
Preventing and treating fungal infections in turtles starts with maintaining a healthy gut microbiota. Here are some recommended practices:
1. Balanced Diet
Providing a balanced and varied diet that resembles their natural food sources can help support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. Including high-fiber foods, such as leafy greens and vegetables, can promote a diverse gut microbiota in turtles.
2. Probiotics
Introducing probiotics, which are beneficial bacterial strains, can help restore and maintain a healthy gut microbiota. Probiotics can be administered orally or added to the turtle’s diet to replenish beneficial bacteria.
3. Reduce Stress
Creating a stress-free environment is crucial for maintaining the overall health of turtles. Proper temperature, adequate lighting, and appropriate habitat conditions can help reduce their stress levels, which in turn benefits their gut microbiota.
4. Minimize Antibiotic Use
When using antibiotics to treat bacterial infections, it is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and duration strictly. Additionally, probiotics can be administered alongside antibiotics to minimize disruption to the gut microbiota.
5. Veterinary Care
Regular veterinary check-ups and consultations are essential for turtles’ well-being. A veterinarian specializing in reptiles can guide nutrition, habitat, and any necessary medical interventions to maintain a healthy gut microbiota and prevent fungal infections.
The gut microbiota in turtles plays a vital role in their overall health, including digestion, immunity, and disease prevention.
A disruption in the balance of beneficial gut bacteria can contribute to the development of fungal infections in their digestive system.
By providing a balanced diet, minimizing stress, and using probiotics when necessary, turtle owners can help maintain a healthy gut microbiota and reduce the risk of fungal infections.
Regular veterinary care is also essential in preventing and addressing any potential health issues related to the gut microbiota in turtles.
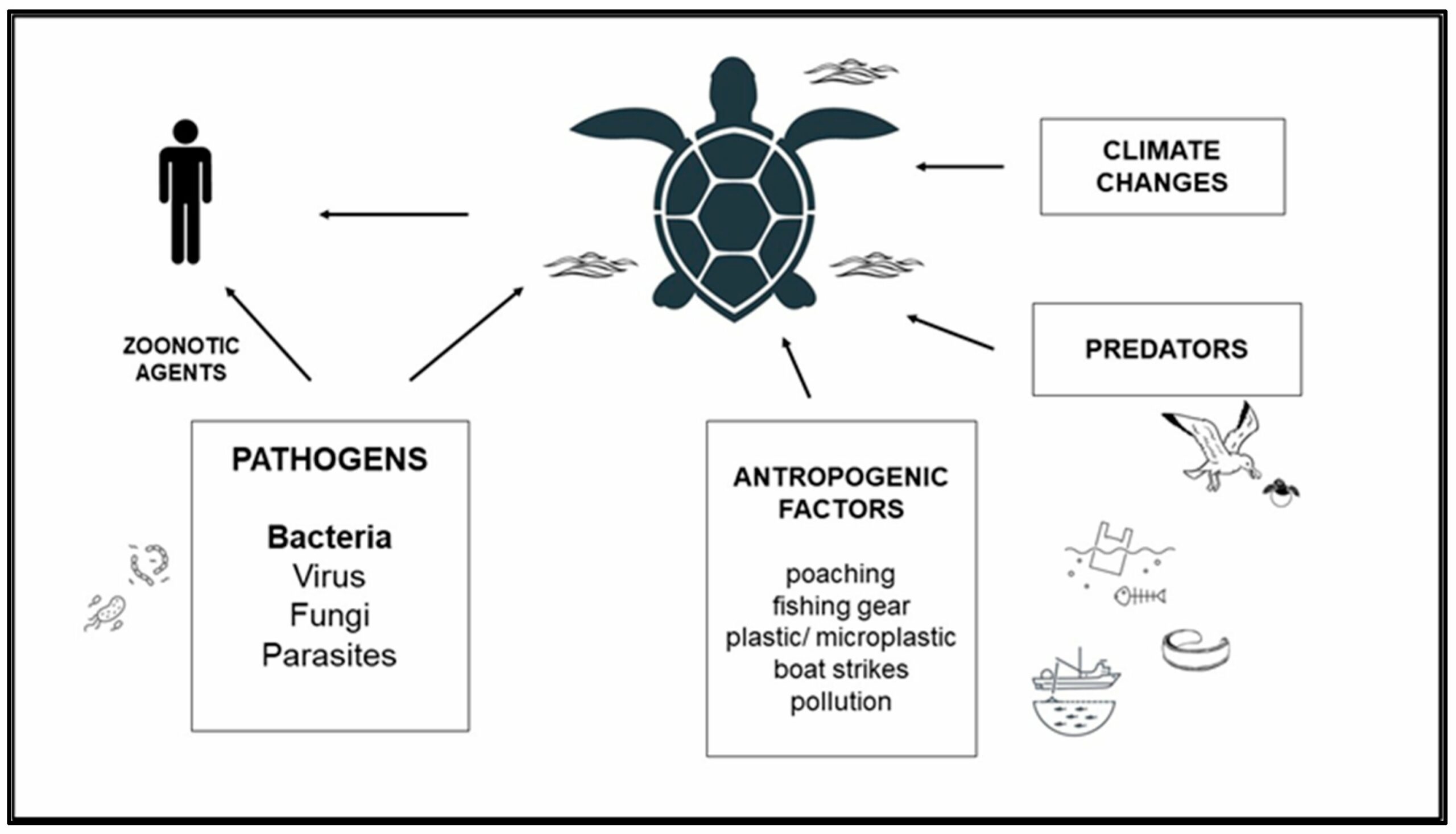
Parasite of Turtles
Faqs for Can Turtles Develop Fungal Digestive Infections:
Yes, turtles can potentially develop fungal infections in their digestive system due to a lack of beneficial gut bacteria. The gut microbiota plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and balance of the digestive system in turtles, just as it does in other animals.
When there is a disruption in this microbial balance, such as a decrease in beneficial bacteria, it can create an environment that is more susceptible to fungal overgrowth. This can lead to various digestive issues and potentially fungal infections in turtles.
Common symptoms of a fungal infection in a turtle’s digestive system may include decreased appetite, weight loss, unusual feces, bloating, increased mucus production, and diarrhea.
It is important to note that these symptoms can vary depending on the specific type of fungal infection and the severity of the case.
If you notice any concerning symptoms or suspect a fungal infection, it is best to consult a veterinarian who specializes in reptile care for proper diagnosis and treatment.
A lack of beneficial gut bacteria in turtles can occur due to various factors. These may include an improper diet lacking essential nutrients, overuse of antibiotics, stress, poor habitat conditions, or a compromised immune system.
Additionally, factors such as inadequate hygiene practices and exposure to contaminated environments can also disrupt the natural balance of the gut microbiota in turtles.
Yes, an imbalanced gut microbiota in turtles can often be treated. The first step is to identify the underlying cause of the imbalance, whether it is due to dietary issues, stress, or other factors.
Treatment options may include dietary adjustments to provide appropriate nutrition, administration of probiotics or prebiotics to encourage the growth of beneficial bacteria and management of any underlying health conditions.
It is important to work closely with a reptile veterinarian to determine the most suitable treatment plan for your turtle.
To promote a healthy gut microbiota in your turtle, it is essential to provide a well-balanced diet that meets their nutritional needs. This typically includes a variety of vegetables, fruits, and appropriate protein sources.
Additionally, maintaining proper hygiene and cleanliness in the turtle’s enclosure, providing a suitable habitat with adequate temperature and humidity, and minimizing stress factors can all contribute to a healthy gut microbiota.
Regular veterinary check-ups and monitoring of the turtle’s overall health are also important for early detection and prevention of imbalances in the gut microbiota.
Final Thoughts
Turtles, like all other animals, can be prone to fungal infections in their digestive system because they lack beneficial gut bacteria. This imbalance can disrupt the delicate gut ecosystem, resulting in an overgrowth of harmful fungi. Without beneficial bacteria to control the fungi, turtles may suffer from digestive problems and potentially develop severe fungal infections. It is therefore essential to maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria in turtles to prevent these infections. By recognizing and addressing the significance of beneficial gut bacteria, we can help promote the overall well-being and health of turtles in their natural habitats.